
Coming back to the New York - Denver example, this means that if the dew point and temperature in both cities are the same, then the mass of water vapor per cubic meter of air will also be the same in those cities. In the same way, increasing the absolute humidity after a temperature drop brings the dew point back up to its initial level. Reducing the absolute humidity will bring the dew point back down to its initial value. If the temperature rises without changing the absolute humidity, the dew point will rise accordingly. For this reason, the same dew point in New York and Denver (which is at a much higher altitude) will imply that a higher fraction of the air in Denver consists of water vapor than in New York.Īt a given temperature but independent of barometric pressure, the dew point indicates the absolute humidity of the air. In the same way, increasing the mole fraction after a pressure drop brings the dew point back up to its initial level. Reducing the mole fraction will bring the dew point back down to its initial value. If the barometric pressure rises without changing this mole fraction, the dew point will rise accordingly.
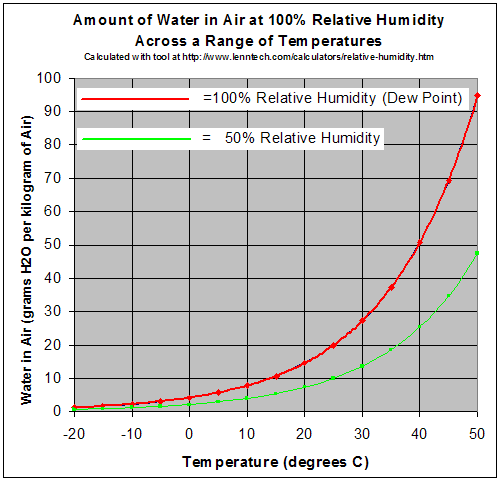
Dew point is a monotonic function of the partial pressure of water vapor, so dew point can be determined from partial pressure of water vapor alone, and vice versa.Īt a given barometric pressure, independent of temperature, the dew point indicates the mole fraction of water vapor in the air, or, put differently, determines the specific humidity of the air. The formation of dew would occur at the dew point even if the only gas present were water vapor. The behavior of water vapor does not depend on the presence of air. With higher temperatures, the equilibrium partial pressure of water vapor increases and more water evaporates. The graph above shows the maximum percentage of water vapor that can exist in air at sea level across a range of temperatures. The dew point is an important statistic for general aviation pilots, as it is used to calculate the likelihood of carburetor icing and fog. Īt a given barometric pressure, independent of temperature, the dew point indicates the mole fraction of water vapor in the air, and therefore determines the specific humidity of the air. It is for this reason that equatorial climates can have low relative humidity, yet still feel humid.
Given a constant dew point, an increase in temperature will lead to a decrease in relative humidity. If the relative humidity is 100%, the dew point is equal to the current temperature. A high relative humidity indicates that the dew point is closer to the current air temperature. The dew point is associated with relative humidity. When the dew point temperature falls below freezing it is called the frost point, as the water vapor no longer creates dew but instead creates frost or hoarfrost by deposition. The dew point (or dewpoint) is the temperature to which a given parcel of air must be cooled, at constant barometric pressure, for water vapor to condense into water.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
